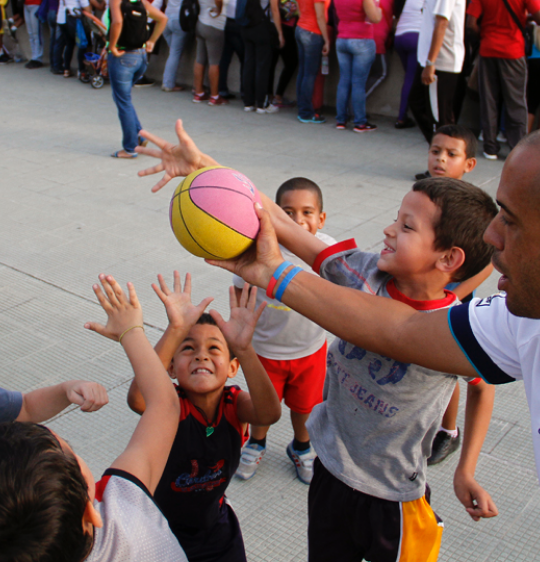
Different guidelines that support programmes related to Sport for All
The Guidelines cover the following sections
For organisations and individuals involved in Sport for All, evaluation provides answers to critical questions: Are we achieving our goals? Are we reaching the people who need us most? Are we contributing to something bigger, such as the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)? With the right tools, we can gather evidence that tells these stories, validates our efforts, and...
Sports have the power to transform lives by fostering physical health, mental well-being and social connections. However, many individuals face significant barriers that prevent them from joining or staying involved in organised sports. These obstacles range from financial and time constraints to social and cultural factors, creating challenges that organisations must address to ensure inclusiveness and sustained engagement. This guide...
The United Nation Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), adopted by 193 countries in 2015, serve as a global blueprint for addressing the world’s most pressing challenges by 2030. These 17 interconnected goals aim to tackle issues like poverty, inequality, climate change, and access to education and healthcare. At the heart of the SDGs are three guiding principles: People, Planet, and...
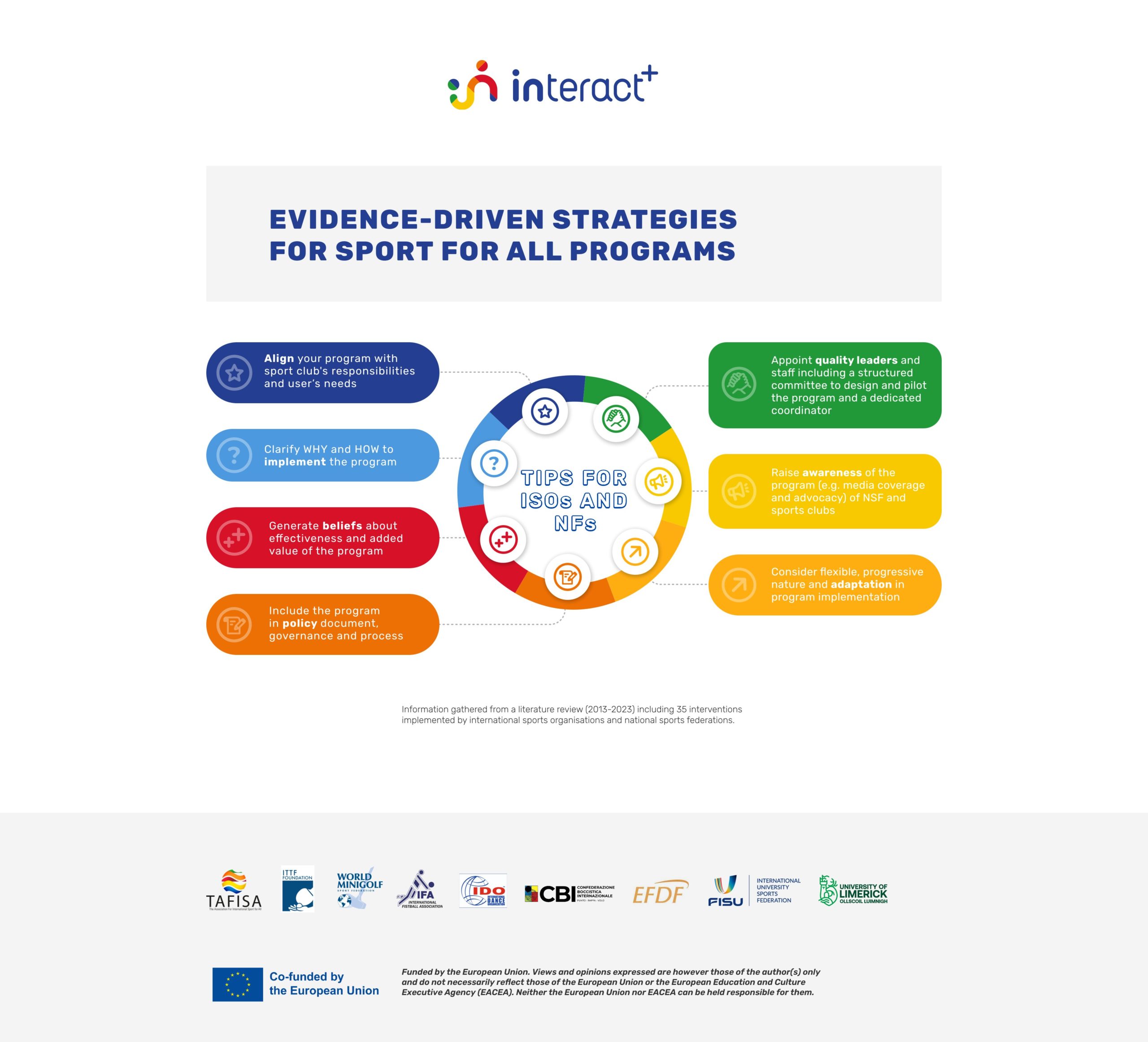
International Sports Organisations (ISOs) and National Federations (NFs) play a crucial role in shaping the future of sports participation and inclusion. However, the traditional focus on elite performance and competitive sports has often sidelined broader social, health, and community-based objectives. The INTERACT+ project aims to bridge this gap by providing ISOs and NFs with the tools and strategic direction...






